A Simple Guide to Publishing Your Research Data
As a researcher in chemistry, sharing the data underlying your published results is crucial for advancing science and ensuring your work is accessible to und can be understood by others. This guide will walk you through the essential steps and considerations for publishing your research data alongside a published paper effectively.
This guide is based on our standards for data publishing for authors. You can view the full list of standards at the end of this article.
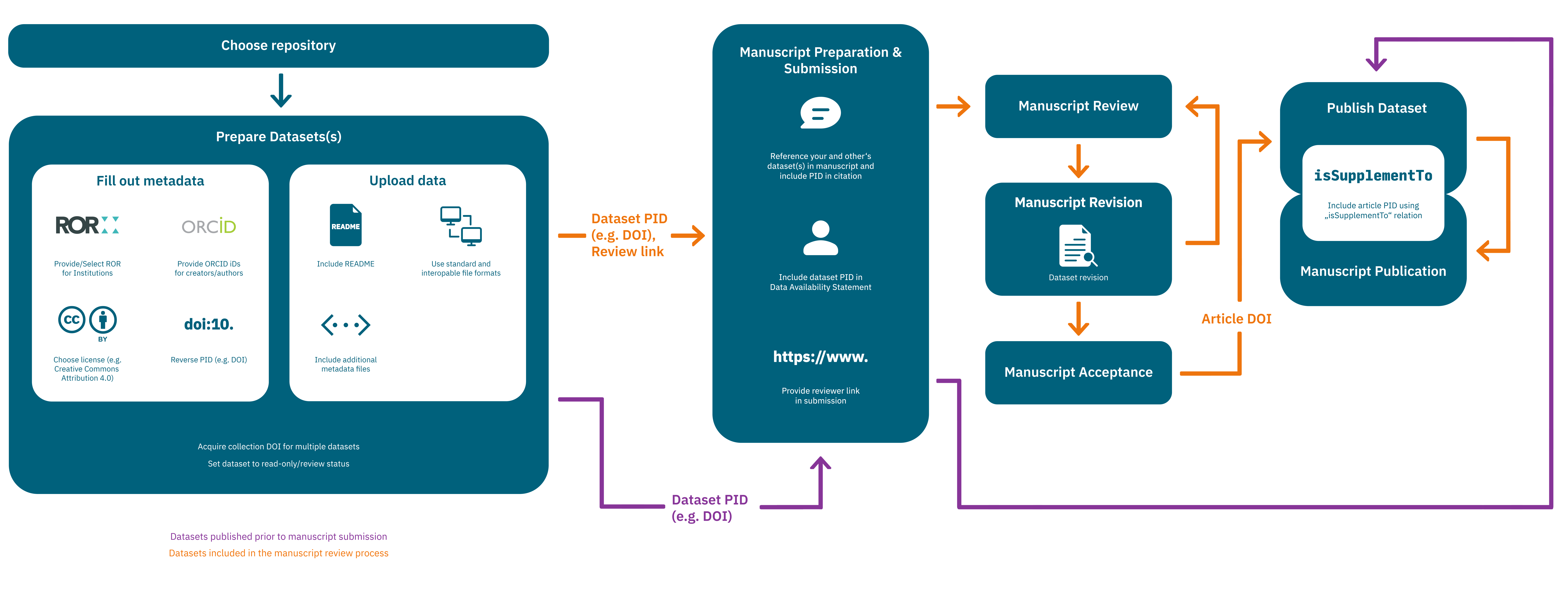
1. Upload your Dataset
Once you have ensured your data is well-organized and you have chosen appropriate data formats, you can upload your files. Depending on the repository you have chosen, it may be easiest to directly upload your data when creating the dataset. For example, RADAR4Chem will automatically extract all files from a zip file at this point and replicate the directory structure, while this is not the case if the data is uploaded at a later point in time and an empty dataset is created first.
Including a plain-text README file within your dataset can give more human-readable context to your data. You may also include additional metadata files if you feel the options offered by the repository are insufficient to give the full context to your dataset.
2. Identify Yourself and Your Institution
Before you publish, make sure to provide your ORCID iD—a unique identifier that helps distinguish you from other researchers. Similarly to article submission systems, most research data repositories provide fields for this information. To get your identifier, simply register yourself through ORCID's registration site.
Additionally, use the ROR identifier (Research Organization Registry) to clearly identify your affiliated institution. Many research data repositories already provide search functionality to autofill this information. Otherwise, find your instition's identifier at ror.org.
These identifiers help improve the visibility of your work.
3. Use Persistent Identifiers (PIDs)
When you deposit your research data, it will be assigned a persistent identifier (PID), similarly to how your article is designated a DOI (Digital Object Identifier). In many cases, the dataset's PID will be a DataCite DOI. Here’s how to use it:
- For Your Own Datasets: Include the PID in the data availability statement of your article, which informs readers where they can find your underlying data. Also, add this PID in the references section of your manuscript to cite it specifically within the text.
- For Others’ Datasets: If you reuse datasets published by other researchers, include their PIDs in your references instead of just citing their articles. This not only gives proper credit but also helps others locate those datasets easily.
This distinction is important, because the link to the dataset in Crossref's DOI metadata for scientific articles varies depending on whether the dataset is a directly related source of information or a specifically referenced resource.
4. Link Your Datasets with Corresponding Articles
To enhance discoverability, link your datasets directly to their corresponding articles:
- Add the article's DOI as a related identifier in the metadata of your dataset when submitting it to a repository.
- Use the relation type
IsSupplementTowhen linking datasets with articles, as recommended by Crossref and DataCite guidelines.
Many repositories will guide you here, offering dropdown menus to select the appropriate relation and identifier type or even automatically detect this information.
5. Utilize Collection DOIs
If you are working with multiple datasets relevant to one article, consider using a Collection DOI provided by repositories:
- Include this Collection DOI in the data availability statement of your manuscript so all related research objects are connected.
- For individual reactions or specific analytical data within those collections, cite them separately with their respective DOIs in both text and reference sections.
6. Choose a License for Your Data
When publishing your research data, it is essential to choose an appropriate license. A license outlines how others can use, share, and build upon your work. Here are some key points to consider when selecting a license:
Why Licensing Matters
Licensing is crucial because it sets the rules for how others can interact with your data. A clear license helps prevent misuse and ensures that you receive proper credit for your contributions. Many repositories will offer a drop-down list of selectable licenses.
Creative Commons Licenses
Creative Commons licenses are widely used for sharing research data and come in various forms:
- CC BY: Allows others to distribute, remix, adapt, and build upon your work, even commercially, as long as they credit you.
- CC BY-SA: Similar to CC BY but requires new creations to carry the same license.
- CC BY-NC: Allows others to use your work non-commercially while still requiring attribution.
How to Choose a License
-
Consider Your Goals: Think about how you want others to use your data. If you encourage widespread use and adaptation, opt for more permissive licenses like CC BY.
-
Understand Legal Implications: Make sure you are comfortable with what rights you are granting by choosing a particular license.
-
Seek Guidance if Needed: If you're unsure which license is best suited for your data, consult with colleagues, contact your local open science or research data management offices, or contact NFDI4Chem's helpdesk. Creative Commons also provides a license chooser to help you here.
Communicate Your License Clearly
Once you've chosen a license, make sure it's clearly stated alongside your dataset when submitting it to repositories. This transparency will help users understand their rights and responsibilities regarding your work. In many cases, this will be handled by the repository itself and you only have to select your chosen license.
7. Ensure Findability and Interoperability
By following these steps—using ORCID iDs and ROR identifiers, employing PIDs correctly, linking datasets appropriately, utilizing Collection DOIs, and selecting a license—you significantly enhance the findability and interoperability of your research data, while communicating how other's may use your work. This means others can easily access and build upon your findings!
When to Publish the Dataset
Deciding when to publish your dataset is an important consideration that can impact both your research and its accessibility. Here are some key points to help you determine the best timing:
1. Include Dataset Review in Manuscript Review
Some repositories may offer a "review status" option. Here, a dataset is set to read only and a provided URL can be given to reviewers in the article submission to allow access to your dataset. This allows reviewers to assess both your reported findings and the underlying data simultaneously, enhancing transparency and reproducibility in your research. By sharing your data during this stage, you provide reviewers with a complete picture of your work, which may lead to more constructive feedback.
If possible, ensure you have reserved a DOI for your dataset so you can provide this during the submission process, as well, while clearly communicating that it is not yet active.
This option allows you to review your dataset and make any requested changes prior to data publication.
In this case, the dataset should be published once the manuscript has been accepted—at the latest once the journal has provided you with a DOI for the manuscript so you can add it to your dataset.
2. Publish Data Prior to Manuscript Submission
In some cases, it might be beneficial to publish your dataset before submitting your manuscript. This approach can establish a clear record of your data and its availability, allowing other researchers to reference or build upon it even before the formal publication of your article.
This allwos you to provide a registered and functioning DOI for the dataset. Many repositories will allow you to alter the dataset metadata, thus adding the article DOI at a later point in time.
If you have placed an embargo on your published dataset, you must ensure that reviewers are given access to the full data. An embargo limits access to the data, while the metadata remains publicly accessible.
Consider Journal Policies
Be aware of any specific policies from the journal you intend to submit to regarding data sharing and publication timelines. Some journals encourage or require authors to make their datasets publicly available prior to or at the time of article submission, while others may have different guidelines.
Ensure Data Quality and Completeness
Before publishing, make sure that your dataset is well-organized, complete, and adequately documented. Providing sufficient metadata will enhance discoverability and usability for other researchers who may want to access or cite your work.
By carefully considering these factors when deciding on the timing for publishing your dataset, you can maximize its impact and facilitate collaboration within the scientific community.
Conclusion
Publishing research data might seem daunting at first, but by following these straightforward guidelines tailored for chemists, you will contribute positively to scientific discourse while ensuring that others can benefit from and verify your work.
Standards
- Authors should provide their ORCID iD to identify the authors/creators and contributors, and their ROR identifier to identify the institution to which they are affiliated.
- Authors should add the PID of their corresponding dataset(s) to the data availability statement and should add PIDs of dataset(s) to the reference section in order to specifically cite dataset(s).
- Authors should include PIDs for datasets published by other researchers that have been reused in the references, rather than citing the corresponding article.
- Researchers should link their datasets to be published to their corresponding articles by adding the article DOI to the dataset's DataCite metadata as a related identifier.
- Researchers should link their datasets to be published to their corresponding articles using the relation type
IsSupplementTo. - Researchers should use the Collection DOI provided by a repository in the data availability statements of their corresponding manuscript to wrap research data objects that are relevant to that of an article to be published.
Main authors: ORCID:0000-0003-4480-8661, ORCID: 0000-0002-6243-2840